Exploring Silver Ore Smelting Techniques and History


Intro
The process of extracting silver from its ore is not just a mere task; it is a blend of art and science that has evolved over centuries. At its core, smelting silver ore involves transforming raw minerals into a pure, usable form of silver, and this narrative weaves through the fabric of history, technology, and even mythology. The journey spans from ancient civilizations, where silver was sacred, to today's modern methods that combine innovation with tradition.
Silver, with its distinct properties, has captivated mankind since time immemorial. Its malleability, conductivity, and lustrous appearance have rendered it precious—not only as currency but also as a key material in art, jewelry, and industry. The smelting procedures vary, reflecting technological advancements and environmental considerations, revealing how humanity has adapted its practices to suit both the times and, increasingly, the planet.
This exploration is not limited to the physical act of smelting itself but delves into the profound implications it has on our world. From the economic timelines of empires that prospered due to silver extraction to the ongoing discussions about the environmental impact of mining and smelting operations, each layer tells a story. Even in the realm of gaming, notably in World of Warcraft, silver ore smelting has its place, mirroring the realities of resource extraction and crafting that players navigate within the game.
Thus, as we embark on this exploration, we wrap our minds around more than just methodical techniques and historical accounts; we engage with a story that carries the weight of civilizations on its back, shaping both our natural and digital landscapes.
Foreword to Silver Ore Smelting
The journey of transforming raw silver ore into gleaming ingots is not just a technical process; it's an art rooted in centuries of history and innovation. Delving into the world of silver ore smelting opens the door to understanding the complex interplay between chemistry and metallurgy that ultimately yields one of the most sought-after metals on the planet.
Understanding silver ore smelting is crucial as it provides insights into how humanity has harnessed natural resources throughout the ages. From ancient civilizations that discovered rudimentary techniques to modern industries employing cutting-edge technology, the evolution of this craft reflects our quest for efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
The importance of studying silver ore smelting lies in its multifaceted nature. Not only does it spotlight the methods of extraction, but it also sheds light on the socio-economic conditions tied to silver production in various cultures. Moreover, for those players immersed in games like World of Warcraft, knowledge of ore smelting enhances gameplay efficiency—making it essential for crafting beautiful gear or trading valuable resources.
Understanding Silver Ore
Silver ore primarily comprises silver sulfide minerals such as argentite and acanthite, alongside other associated minerals like lead and copper. The complex composition demands a clear understanding of its properties to optimize smelting techniques. Recognizing local geology can greatly influence mining strategies, which, in turn, affects the purity and yield during the smelting process. The extraction of silver can significantly differ based on the environmental conditions and mineralogy of the ore, making it a unique challenge.
Usually found in veins alongside other minerals, silver ore often necessitates a detailed analysis to ensure that it is indeed worth the extraction efforts. Identifying the right type of ore not only determines the potential yield but also influences the choice of smelting methods to employ, impacting overall efficiency.
Historical Context of Silver Extraction
Silver extraction traces back to ancient civilizations, with archaeological evidence showing practices in places like Anatolia and Persia as early as 3000 BC. During these times, silver was not just a form of currency but held significant cultural and religious value. Techniques were rudimentary; however, these early experiments were pivotal in paving the way for future advancements.
As societies developed, so too did the practices surrounding silver extraction. The Romans brought engineering marvels to smelting operations, using sophisticated furnace designs that improved yields significantly. The Middle Ages saw a boom in silver mining, leading to significant economic shifts in Europe. In places like Mexico and Bolivia, colonial extraction efforts brought about both wealth and suffering, illustrating the duality of silver as a resource—one that drives economy but often at a moral cost.
In the more contemporary context, understanding this rich history is vital. It provides a foundation for the modern practices we see today, shedding light on the environmental and economic ramifications of silver extraction that still resonate in the 21st century. Knowledge of these historical techniques can enrich a gamer's experience, especially when engaging with lore and quests that revolve around resource gathering and processing in virtual worlds.
The Composition of Silver Ore
Understanding the composition of silver ore is vital for grasping the smelting process itself. This section not only touches upon the intricate makeup of silver ore but also emphasizes the connection between its chemical structure and its extraction methods. Recognizing the mineral content and the properties of different types of silver deposits can significantly influence how silver is mined and processed.
Mineral Composition and Types
Silver ore isn't a one-size-fits-all kind of deal. It varies widely in its mineral composition, but some common elements are often present, like sulfides and carbonates. These minerals can dictate the extraction method employed, as well as the overall yield of silver.
- Argentite (Ag2S): This is a silver sulfide mineral and is one of the most important silver ores. Its high silver content makes it a prime target for extraction.
- Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2): While primarily a copper ore, it also contains silver in noteworthy quantities, making it valuable in mixed ores.
- Galena (PbS): Often containing silver in its composition, galena can be associated with lead mining, which is why the two are commonly mined together.
- Native Silver (Ag): Sometimes, you might find silver in a pure state, which is relatively rarer but can be quite rewarding when located.
Each type of mineral requires a slightly different approach to extraction. Having a clear understanding of these minerals enhances the efficiency of the smelting operation, making it more productive while minimizing costs.
Identifying Silver Deposits
Identifying where to find silver deposits isn't just a matter of luck; it involves a blend of geology and practical knowledge. There are key indicators that miners look for, often referred to informally as the 'silver signs.'
- Geological Mapping: This is akin to creating a treasure map, using geological surveys and past mining reports to pinpoint areas with potential.
- Geochemical Analysis: Soil and rock samples are analyzed for trace elements associated with silver. A concentration of lead, copper, or zinc can suggest nearby silver deposits.
- Topographical Features: Valleys and ridges can reveal hidden resources. Ancient riverbeds often washed away elements that contributed to the concentration of silver ores in certain areas.
- Activity of Other Miners: Observing where silver has been historically extracted can offer hints about new deposits.
By employing a mix of these methods, miners can not just randomly dig dirt. Instead, they strategically hunt for silver, ensuring their efforts are as fruitful as possible.
Silver mining is not strictly about the technical aspect; much of it is based on intuition and decades of practice passed on through generations. The art of identifying the right deposits is just as integral to successful smelting as the science of the smelting process itself.
The success in mining silver lies at the intersection of thorough knowledge and intuitive skill.
Techniques in Silver Smelting
Smelting silver ore is not just a science; it’s an art. The techniques used in smelting vary widely, each playing a crucial role in the efficiency and effectiveness of the extraction process. Understanding these techniques is essential for both historical and modern contexts, as they shape how we recover silver from its raw forms while considering economic feasibility and environmental impact. This section delves into the conventional and contemporary methods employed in silver smelting, highlighting the evolution of practices and the reasons behind these developments.
Traditional Methods of Smelting
Before the age of modern technology, silver smelting was rooted in traditional practices that have stood the test of time. These methods are often passed down through generations and come with their own set of challenges and rewards.
- Cupellation: One of the oldest forms of smelting, cupellation involves the use of a furnace to separate silver from lead. The lead ore is heated, and when it reaches melting point, silver separates and is collected. This method has been used since ancient times and is still appreciated for its simplicity and effectiveness.
- Fire Assay: This method involves mixing crushed ore with fluxes to create a slag that separates from the molten silver. Although it requires a specific temperature that can be tricky to maintain, the fire assay remains a standard in determining the purity of ore.
- Poling: This technique uses wood to stir molten metal, which helps eliminate unwanted elements while enhancing silver purity. Here, the way the metal mixes with air effectively improves quality.


The key takeaway from these traditional methods is their adaptability. They may not always be the most efficient, but they reflect years of wisdom and experience. The controlled environment allows for a degree of finesse that modern techniques sometimes lose sight of.
Modern Smelting Technologies
Fast forward to today, and silver smelting has integrated sophisticated technologies that optimize the recovery process. These advancements have enabled processing facilities to increase yield while reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Induction Furnaces: These allow for precise temperature control, which can be adjusted based on the properties of the ore. Induction heating reduces contamination, making it a popular choice among modern facilities.
- Hydrometallurgy: By using aqueous solutions, this technique allows silver to be extracted without the use of harsh chemicals. It represents a significant leap towards environmentally-friendly practices in the silver mining industry.
- Electrolytic Refining: A process employed to further purify extracted silver, electrolytic refining uses an electrolytic cell to deposit pure silver onto cathodes. It is a preferred method for recycling silver due to its efficacy.
Applications of these advanced techniques are essential, especially as the market demand for silver rises and becomes more competitive. The shift towards modern methodologies has not only increased production but has also brought forth practices that consider the environmental aspect of smelting, ensuring sustainability.
To sum it up, the techniques of smelting silver ore have transitioned from age-old practices to modern technologies. Each method plays an important role, each with its own benefits and complexities. The ongoing evolution of these techniques indicates a commitment to improvement—whether that is in terms of yield, purity, or environmental impact.
These avenues allow for a greater understanding of what is required to excel within this field, especially for those immersed in gaming and fantasy universes like World of Warcraft, where silver holds distinct value.
The Smelting Process Explained
The smelting process for silver ore lays down the groundwork for converting raw silver-bearing materials into a usable form. It encompasses several crucial steps from preparation to the application of high temperatures that ultimately yield silver. Understanding this process is important not only for its practicality but also for appreciating the science and artistry behind it.
Preparation of Ore
Before the smelting can even begin, the silver ore must undergo rigorous preparation. This phase is about more than just mining the ore; it involves several preliminary steps that can significantly influence the quality and quantity of silver extracted.
First, miners must crush and mill the ore to liberate the silver from other minerals. The grinding must be thorough, breaking the ore into smaller pieces so that the smelting furnace can efficiently process it. A common method involves using ball mills, where steel balls grind the ore down to a fine powder.
Next, the powdered ore may require concentration. This could involve flotation, where chemicals are added to separate valuable minerals from waste material, or using gravity separation methods like jigging. The result is a more concentrated form of silver ore, often referred to as "concentrate." This step is essential not only for improving the yield but also for minimizing energy usage in subsequent smelting processes.
Furnace Types and Their Uses
With the ore prepared, it is time to select the right furnace for the smelting operation. Different furnace types serve varying purposes based on the scale and efficiency needs of the smelting process.
Among the commonly used furnaces are:
- Blast Furnaces: Ideal for large-scale operations, they work by forcing air through the material to ignite the fuel and provide the high temperatures necessary for smelting.
- Induction Furnaces: These utilize electromagnetic induction to heat the material directly, allowing for precise temperature control and faster processing.
- Reverberatory Furnaces: Here, the heat is reflected down onto the ore from the furnace ceiling, which allows the operator to smelt multiple materials at once.
Each type of furnace has its string of advantages, from the initial cost to the level of energy consumed. Choosing the right furnace is akin to selecting the right equipment for a battle—it can make or break the success of the operation.
Fluxing Agents Role
Fluxing agents are the unsung heroes of the smelting world. These materials are added to the ore during the smelting process to aid in the separation of the desired metals from unwanted impurities. Without fluxes, the process can be less efficient and result in a significant loss of precious silver.
Common fluxing agents include:
- Borax: It lowers the melting point of the ore, preventing the formation of a dense slag that could entrap silver particles.
- Lime: Acts as a chemical reagent to help neutralize acids, facilitating better separation of metals from non-metallic impurities.
- Soda Ash: This helps in reducing the viscosity of the molten material, making it easier to remove slag.
The careful choice and precise amount of fluxing agents play a pivotal role in determining the recovery rates of silver in the final product.
Temperature Control and Results
When smelting silver ore, temperature holds the key to unlocking the metal's potential. The smelting process requires specific temperatures to melt the ore and facilitate the separation of silver from impurities. Generally, temperatures must reach around 1,000°C to effectively smelt silver ores.
In modern smelting operations, precise temperature control can make the difference between a successful extraction and a failed batch. Factors like furnace type, ore quality, and flux employed influence the optimal temperature settings.
Once reached, the temperature allows the silver to melt thoroughly, separating it from the unwanted slag that floats on the surface. After the smelting, the resulting molten silver can be poured into molds for cooling.
"Temperature is the silent sentinel in the smelting realm; too low, and the job isn’t done; too high, and you risk losing your treasure."
This careful dance around the furnace's heat is what turns raw ore into shimmering bars of silver, ready for use in jewelry, electronics, and beyond.
By understanding this intricate process, those involved in smelting can not only enhance their techniques but also appreciate the delicate balance of art and science that silver smelting embodies.
Safety Precautions in Smelting
When it comes to smelting silver ore, safety is no more a luxury than it is a necessity. Engaging in such industrial processes without the right precautions can lead to serious accidents, injuries, or even long-lasting health issues. The art of smelting not only involves technique and skill but also a keen awareness of the potential dangers lurking in the smoke and fire. Proper safety measures enhance the efficiency and enjoyment of smelting while minimizing risks, so let’s dive into the various elements that reinforce safety in this craft.
Protective Gear
The first line of defense for anyone involved in silver smelting is protective gear. This gear isn’t just about looking the part; it serves to protect against burns, inhalation of toxic fumes, and potential eye damage. Standard protective equipment typically includes:


- Face Shield: A vital component that guards your face against flying debris and harmful fumes. Make sure it’s rated for high temperatures.
- Gloves: Opt for heat-resistant gloves to handle molten material safely. Heavy-duty options made from leather or special heat-resistant materials are vital in protecting your skin.
- Apron: A thick apron can shield your body from splashes of molten metal and other hazards that may come from your workstation.
- Respirators: Given that smelting can release dangerous fumes like sulfur dioxide, a quality respirator fitted with the proper filters is essential for maintaining lung health.
It's not just about showing up looking like a pro, but it's a matter of survival when you’re dealing with this level of heat and potential danger. Remember, even a small lapse in safety can turn a seemingly minor task into a dangerous ordeal.
Handling Hazardous Materials
Smelting involves various hazardous materials that pose significant risks if not handled correctly. Silver ore often contains other metals like lead and arsenic, both of which can present serious health risks. Understanding how to manage these materials is of utmost importance. Here are some crucial points to bear in mind:
- Storage: Store hazardous materials in clearly labeled containers, and ensure your workspace is free from spills and clutter that could lead to accidents.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Having the SDS for all materials on hand offers insights on potential hazards and appropriate emergency measures. Familiarize yourself with these documents; they could be lifesavers in emergencies.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of any waste properly. Many materials used in smelting are hazardous, so adhering to local regulations on disposal is essential.
- Ventilation: The workspace should be well-ventilated. This helps to disperse harmful fumes and keep the air quality safe for inhalation, especially when handling materials that might cause respiratory issues.
"Safety isn't just a priority; it's a necessity. Without it, you're playing with fire — literally!"
By maintaining a strict regimen of safety precautions, smelting becomes not only a manageable task but also an enjoyable process. There’s no denying that the stakes are high in the world of smelting; however, with the correct gear and diligent handling of materials, we can significantly mitigate those risks, making the journey of silver extraction a much safer endeavor.
Environmental Impact of Silver Smelting
Understanding the environmental impact of silver smelting is crucial, especially in today's world where sustainability is becoming a pressing issue. The smelting of silver ore, while beneficial economically, carries a variety of environmental considerations. It’s essential to explore not just the pollution concerns but also sustainable alternatives that can help mitigate the negative effects associated with traditional silver extraction methods.
Pollution Concerns
The smelting process, by its very nature, involves the release of various pollutants into the atmosphere and local ecosystems. When silver ore is heated at high temperatures, it leads to the emission of sulfur dioxide, heavy metals, and other particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to acid rain, which adversely affects soil, water bodies, and vegetation.
In addition, if proper waste management strategies aren’t implemented, toxic byproducts can leach into nearby water sources. This poses not only a risk to aquatic life but also to public health, especially in communities that might rely on these water sources for drinking, cooking, and agriculture. Stakeholders need to take note of these impacts, particularly in regions where silver mining is a significant industry.
- The significant pollutants from silver smelting include:
- Lead: Contributes to soil contamination and health issues.
- Arsenic: Known for its toxicity, especially in drinking water.
- Cadmium: Effects include respiratory issues and various cancers.
Implementing proper monitoring and stringent regulations can help in curbing these emission levels, but it requires concerted efforts from both the industry and regulatory bodies to establish a framework that prioritizes environmental safety.
Sustainable Alternatives
The demand for more sustainable practices has led to innovations in silver extraction processes. One exciting avenue is the development of bioleaching techniques, where microbes are used to extract metals from ores. This not only minimizes the environmental footprint of silver smelting but also potentially reduces costs associated with energy-intensive traditional methods.
Some other sustainable practices include:
- Recycling Silver: Recovering silver from electronic waste and old jewelry can significantly reduce the need for primary mining.
- Responsible Sourcing: Ensuring that silver comes from mines that adhere to environmental standards can help alleviate some impact.
- Alternative Materials: Research and use of substitutes that mimic silver in appearance and function can reduce overall demand.
"Investing in sustainable technology is not just a choice; it’s a necessity for the future of silver processing. It’s high time that industry players become proactive in adopting eco-friendly practices."
Navigating the balance between economic benefit and environmental responsibility presents both challenges and opportunities for the silver smelting industry. As the world becomes increasingly eco-conscious, these sustainable alternatives will likely shape the future landscape of silver ore processing, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
Economic Considerations
The economic factors surrounding silver smelting are as essential to the process as the technical methods involved. Understanding the costs associated with extracting and processing silver ore can give insights into the viability and profitability of a smelting operation. From initial investments to operational expenses, various elements coexist to shape the economic landscape of silver production.
Cost Analysis of Smelting
When it comes to smelting silver, the overall cost analysis includes both direct and indirect expenses. Direct costs typically cover the hardware, such as smelting furnaces and associated equipment, which can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. Additionally, consumables like fluxing agents and other chemicals also contribute to the cost.
On top of material costs, labor must not be overlooked. Skilled labor is required to monitor the smelting process, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and safely. Training personnel adds another layer of expense. As a result, before diving into production, potential smelters are encouraged to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis.
- Fuel Expenses: One of the largest ongoing costs in silver smelting is fuel. Different furnaces require various types of fuel, be it coal, natural gas, or electricity. As fuel prices fluctuate, so do the operational costs.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Equipment degradation can knock a smelting operation out of alignment if not addressed quickly. Therefore, setting aside a budget for routine maintenance and potential upgrades is necessary.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: Regulations surrounding environmental factors also affect smelting costs. Smelting operations may have to invest in pollution control systems or pay fines if standards are not met.
In the long run, streamlining these costs through efficient practices can significantly enhance profitability and attract further investments.
Market Trends for Silver
The market dynamics of silver are influenced by numerous factors including demand, investment trends, and broader economic conditions. Investors often turn to silver as a haven in times of economic uncertainty, which inherently drives up demand. Fluctuations in jewelry production, technological advancements, and the rising necessity for silver in electronics and solar energy contribute to the overall demand landscape.
Currently, we observe some notable trends in the silver market:
- Rising Use in Technology: With the advent of electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions, silver has found a new niche in these rapidly growing sectors. The increased need for conductivity continues to push demand beyond traditional uses.
- Investment Interest: As global markets ebb and flow, investment interest in silver continues to surge, especially amongst those who wish to diversify portfolios. Bullion and coins have remained popular among individual investors.
- Economic Recovery Phases: During recovery periods, there’s often a spike in silver demand driven by industrial needs. This can lead to increased ore smelting as facilities cater to growing production requirements.
"Understanding the market trends is crucial for any entity involved in the smelting or investment of silver. The more informed the decisions, the better the potential returns."
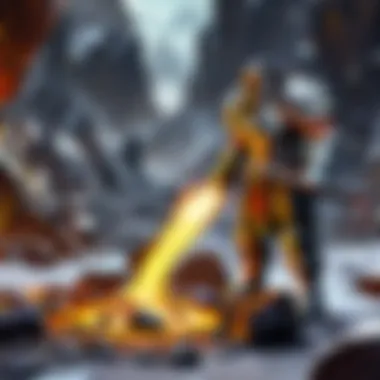

Given these factors, it becomes clear that an efficient smelting operation not only requires a solid understanding of your costs but also staying in tune with market trends. Recognizing how both elements interplay can help businesses navigate the complexities of silver extraction and positioning in the marketplace.
Cultural Significance of Silver
Silver has held a profound place in cultures across the globe, transcending mere currency to become a symbol of purity, prosperity, and power. Its allure doesn't just stem from its shiny appearance but also from the stories and meanings that shape its identity throughout history. In this section, we will explore the nuanced significance of silver in various cultures, as well as its representation in art and literature, especially for those fascinated by the gaming universe.
Symbolism in Different Cultures
Across the ages, silver has been more than a functional metal; it is steeped in rich symbolism. In many cultures, it represents the moon, standing for the feminine and the nurturing. For example, in ancient Egyptian mythology, silver was associated with the moon goddess Isis. The metal was considered a gift from the gods, believed to possess healing properties. It was often integrated into jewelry and talismans designed to ward off evil spirits.
In Asian cultures, silver carries connotations of wealth and good fortune. In China, giving silver gifts is a common practice during celebrations, symbolizing blessings and prosperity. The adage "The more silver you give, the more luck you receive" resonates with countless families, especially during the Lunar New Year.
Moreover, Native American traditions often view silver as a sacred element. Tribes such as the Navajo incorporate silver into their crafts, believing that it connects them with the earth. Silver jewelry often carries meanings tied to personal and communal identity, homelessness indicating strength and resilience. In contrast, in Aztec civilization, it served as a valuable resource in trade.
"To the indigenous people of the Americas, silver isn’t just a precious metal; it’s a thread connecting them to their ancestors and beliefs."
Representation in Art and Literature
The influence of silver extends beautifully into various forms of art and literature. Artists often employ silver to convey themes of purity, beauty, and sometimes even betrayal. In the visual arts, silver leaf is commonly used in paintings and sculptures to enhance aesthetics and impart an ethereal glow.
In literature, silver serves as a multifaceted metaphor. From the pages of classical works to modern fantasy worlds, silver often symbolizes hope, renewal, or even danger, depending on the narrative context. In J.R.R. Tolkien's works, for instance, silver arrows are wielded as symbols of elves' grace and precision, emphasizing their connection to the natural world and magic. Similarly, in many fantasy games, including World of Warcraft, silver commonly illustrates currency, highlight treasure hunts, and quests, shaping gamers' experiences.
In summary, silver's cultural significance is deeply intertwined with both historical rituals and contemporary narratives. Whether it serves as an emblem of wealth, purity, or protection, its multifaceted representations in cultures worldwide underline the continuous impact of silver, reminding us of its value beyond the material. This makes it a subject not only worthy of study but also a key element that enriches the gameplay experience for players, especially in immersive settings like World of Warcraft.
Comparative Analysis with Other Metals
Comparing silver to other metals like lead, zinc, and gold highlights not just the unique qualities of silver but also its versatility in smelting techniques. Each metal behaves differently in processing, so understanding these differences is crucial for both industrial applications and for enthusiasts, particularly gamers who are vested in the economics of resources in games like World of Warcraft. This section lays out what makes silver distinct, the challenges in its recovery, and how that contrasts with other metals that share the limelight in smelting operations.
Lead and Zinc vs. Silver
When we pit lead and zinc against silver, the differences in smelting methods come to the forefront. Lead is generally more abundant and cheaper, which makes its extraction straightforward. The lead ores, such as galena, require a simple smelting process that involves adding carbon to reduce lead oxides.
On the other hand, silver extraction can be more complicated. Silver often exists as a byproduct in lead and zinc ores. When smelting lead, silver may be recovered in a later stage, which means its purity can be tricky. Here are a few points to consider when comparing silver to lead and zinc:
- Market Demand: Silver has always held value, often seen as a safe asset. Lead and zinc, although necessary for various industries, don’t match silver’s sheen in popularity.
- Environmental Impact: Silver extraction can introduce more environmental challenges, with pollutants generated during the smelting process.
- Purity and Quality: While the extraction of lead and zinc might yield more quantity, silver's quality often trumps due to stringent refinement processes like cupellation.
In essence, while lead and zinc may be simpler to extract in bulk, silver’s allure lies in its quality and intrinsic value.
Gold Smelting Techniques
When considered alongside gold, silver shares some smelting principles but diverges significantly in methodology and results. Gold smelting, for instance, is known for its high value and purity standards, much like silver. However, certain aspects differentiate the two:
- Methodologies: Gold is often extracted using techniques such as cyanidation, which can be more chemically intensive than the methods typically employed for silver, like furnace smelting. The sophisticated processes required for gold often necessitate careful measurement of chemicals involved, whereas silver’s processes can be more straightforward.
- Temperature Variance: The melting point for gold (approximately 1,064°C) is higher than that of silver (approximately 961°C). This variance requires different furnaces and temperature controls, a factor worth considering in any comparative study.
- Cultural Relevance: In many cultures, gold has been the symbol of wealth and prosperity, while silver often paves paths in jewelry and electronics; gamers sometimes prefer gold for its utility in high-end crafting materials, but silver cannot be overlooked as it often aids in diverse gameplay elements such as trade and enchantments.
Through these lenses, it’s clear that while silver might seem overshadowed by lead, zinc, and gold, its own unique position in both historical and modern contexts sets it apart in the world of metallurgy. Understanding such nuances not only enriches our knowledge but also influences decision-making in resource management, whether in a gameplay scenario or in a real-world application.
"In metallurgy, the value of each metal is not just in its physical properties, but also in its cultural significance and economic impact."
Sifting through these comparisons allows one to appreciate where silver stands in the grand scheme of metals. Assessing silver’s role helps aim strategic decisions in gameplay scenarios seen in titles like World of Warcraft.
Case Studies
When it comes to silver smelting, case studies provide a window into the past and present practices, highlighting the successful methods and challenges faced by different operations. These real-world examples paint a clearer picture of how smelting processes have evolved over time and offer insights that can be beneficial to both enthusiasts and professionals in the field.
Historical Silver Mines
Throughout history, silver mines have been the heartbeat of various civilizations, truly shaping economic landscapes and cultural identities. Take the ancient Roman mines in Spain, for instance, where operations like Las Médulas became famous for their advanced hydraulic techniques around the first century AD. This site didn't just produce silver; it transformed the way mining was approached. The river diversion and channeling techniques were groundbreaking and would influence mining practices for centuries.
Another notable example includes the Potosí mines in Bolivia, which, during the Spanish colonial period, produced an astronomical amount of silver. By the 16th century, Potosí was a thriving city, built on the backs of ore extracted from the surrounding mountains. Here, the ventilation shafts and refining techniques showcased the ingenuity of miners, as they extracted silver from osmer ores, contributing to the global economy at a time when silver was literally worth its weight.
Such historical mines not only represent the technical prowess of their era but also tell stories of cultural significance and the exploited labor behind the scenes. The case studies from these historic operations remind us that smelting silver is deeply intertwined with social implications, both good and bad.
Contemporary Silver Processing Facilities
Fast forward to today, and our silver processing facilities have become more scientifically advanced, yet they still adhere to the core principles established centuries ago. For instance, the Fresnillo PLC’s operations in Mexico employ state-of-the-art technology combined with time-tested methods of smelting. This facility showcases how modern smelters are not only focused on yield but also increasingly concerned about sustainable practices.
These facilities often utilize advanced leaching processes and sophisticated melting furnaces that allow for better recovery rates, all while minimizing ecological footprints. The implementation of closed-loop water systems to avoid wasting precious resources exemplifies how contemporary operations have adapted to growing environmental concerns.
The data gathered from contemporary case studies can signal trends in market demand, technological advancements, and also highlight areas ripe for improvement or research.
„Case studies act like a compass, pointing current practices towards the future, while keeping a respectful eye on the past.”
Ultimately, the examination of both historical and contemporary silver mining practices not only enriches our understanding of silver smelting but also informs future advancements in the field. Thus, diligent research into these operations becomes an ever-relevant pursuit for those who aspire to delve deeper into the art and science of silver smelting.







